Effects of Chewing Gum on Your Teeth
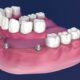
How To Prepare For All-on-4 Dental Implant Surgery
January 15, 2024
How does teeth whitening work?
January 29, 2024Chewing gum is a common habit for many people, but have you ever wondered about its effects on your teeth? In this blog post, we will explore the potential impact of chewing gum on your oral health. Understanding how chewing gum may affect your teeth can help you make informed decisions about this everyday habit. Let’s delve into the potential effects of chewing gum on your teeth.
What is chewing gum?
Chewing gum is a pliable, rubbery substance designed for chewing without being swallowed.
While recipes may differ among brands, all chewing gums share fundamental ingredients:
- Gum: This is the indigestible, rubbery base providing a chewy texture to gum.
- Resin: Typically included to reinforce gum and maintain its cohesion.
- Fillers: Substances like calcium carbonate or talc are employed to impart texture to gum.
- Preservatives: Added to prolong shelf life, often using an organic compound like butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT).
- Softeners: Utilized to preserve moisture and prevent gum hardening, including substances like paraffin or vegetable oils.
- Sweeteners: Popular sweeteners include cane sugar, beet sugar, and corn syrup. Sugar-free gums may contain sugar alcohols like xylitol or artificial sweeteners such as aspartame.
- Flavorings: Natural or synthetic flavorings are introduced to achieve the desired taste.
Manufacturers typically keep the exact gum-making recipes confidential, referring to their specific combination of gum, resin, filler, softeners, and antioxidants as their “gum base.”
Is Chewing Gum Good for Your Teeth?
Yes, provided that it’s the appropriate kind. Tooth decay can be avoided by chewing gum, provided that the gum is sugarless. Chewing gum increases saliva production, which helps wash away and neutralize some of the acid that is left in your mouth after breaking down food. Therefore, chewing gum after a meal may contribute to oral health and tooth protection.
Additionally, the minerals produced by the increased saliva can even aid in fortifying your tooth enamel, hence lowering your chance of developing dental cavities.
Is Sugar-Free Gum Bad for Your Teeth?
This dental hygiene tip can be shared by parents with their frequently gum-chewing children and teens. Just make sure kids select sugar-free gum rather than sugar-filled bubble gum, which can have the reverse effect and worsen plaque accumulation on teeth. Therefore, if you’re not sure which gum is ideal for maintaining dental health, get yourself or your family some sugarless gum.
However, keep in mind (and tell kids) that gum—even sugarless gum—does not replace a consistent oral hygiene regimen that includes brushing your teeth twice a day and properly flossing every day using high-quality dental products.
What happens if you chew gum every day?
Excessive gum chewing may lead to various issues, including jaw pain, headaches, diarrhea, and tooth decay. It’s important to note that the consumption of sugar-free gum can exacerbate digestive symptoms, particularly in individuals with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). If you experience persistent dental concerns related to gum chewing, consider consulting with a dental professional for personalized advice. Dr. Olivia Cui, a dentist in Olds, AB, can guide you on maintaining optimal oral health and address any specific concerns you may have.
Which chewing gum should you choose?
If you enjoy chewing gum, it’s advisable to opt for sugar-free gum sweetened with xylitol.
However, individuals with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) should be cautious as sugar-free gum contains FODMAPs, potentially leading to digestive issues for those with IBS.
For individuals sensitive to FODMAPs, selecting a gum sweetened with a low-calorie sweetener like stevia is recommended.
Before making a choice, carefully review the ingredient list on the gum packaging to ensure it doesn’t contain any ingredients to which you may be intolerant. Seeking guidance from a dentist or dietitian can assist in determining the most suitable type of gum for your needs.
If you happen to swallow gum, be assured that it doesn’t take seven years to digest; your body can safely pass gum within a few days.
Nevertheless, it is not advisable to swallow large amounts of gum. Research indicates that significant gum consumption can result in intestinal blockages, particularly in children. This risk is heightened when a substantial quantity of gum is ingested at once or when someone frequently swallows gum, leading to the formation of a large, indigestible mass known as a bezoar.
It is crucial for individuals of all ages, especially children, to avoid swallowing gum due to the potential choking hazard. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends refraining from giving gum to young children until they can comprehend the instruction not to swallow it.
Repetitive gum swallowing may cause:
1. Abdominal pain
2. Chronic constipation
3. Gas
4. Diarrhea
5. Mouth ulcers
Furthermore, habitual gum chewing can contribute to jaw and dental problems.




